GitHub Integration
Connect and manage your GitHub repositories with Tetrix AI
Overview
The GitHub integration is the foundation of Tetrix AI's contextual understanding. By connecting your repositories, Tetrix can:
- Analyze Code Structure: Understand classes, functions, and their relationships
- Map Dependencies: Track imports, function calls, and data flows
- Identify API Endpoints: Catalog all routes and their implementations
- Understand Database Schemas: Recognize ORM models and queries
- Track Real-Time Changes: Automatically update when code is pushed
- Support Multi-Repo Systems: Analyze dependencies across multiple repositories
Required Permissions
Tetrix requests the following GitHub permissions:
- Read access to repositories: To analyze code structure and content
- Webhook management: To receive notifications when code changes (create, update, delete webhooks)
Tetrix never modifies your code or writes to your repositories. All access is read-only except for webhook configuration.
Why Webhooks?
Webhooks allow Tetrix to:
- Receive instant notifications when you push code
- Automatically update the Knowledge Graph with changes
- Keep your AI assistant's understanding current
- Avoid manual synchronization
First-Time Setup
Your first GitHub connection happens during onboarding. If you haven't completed onboarding yet, see our Quickstart Guide.
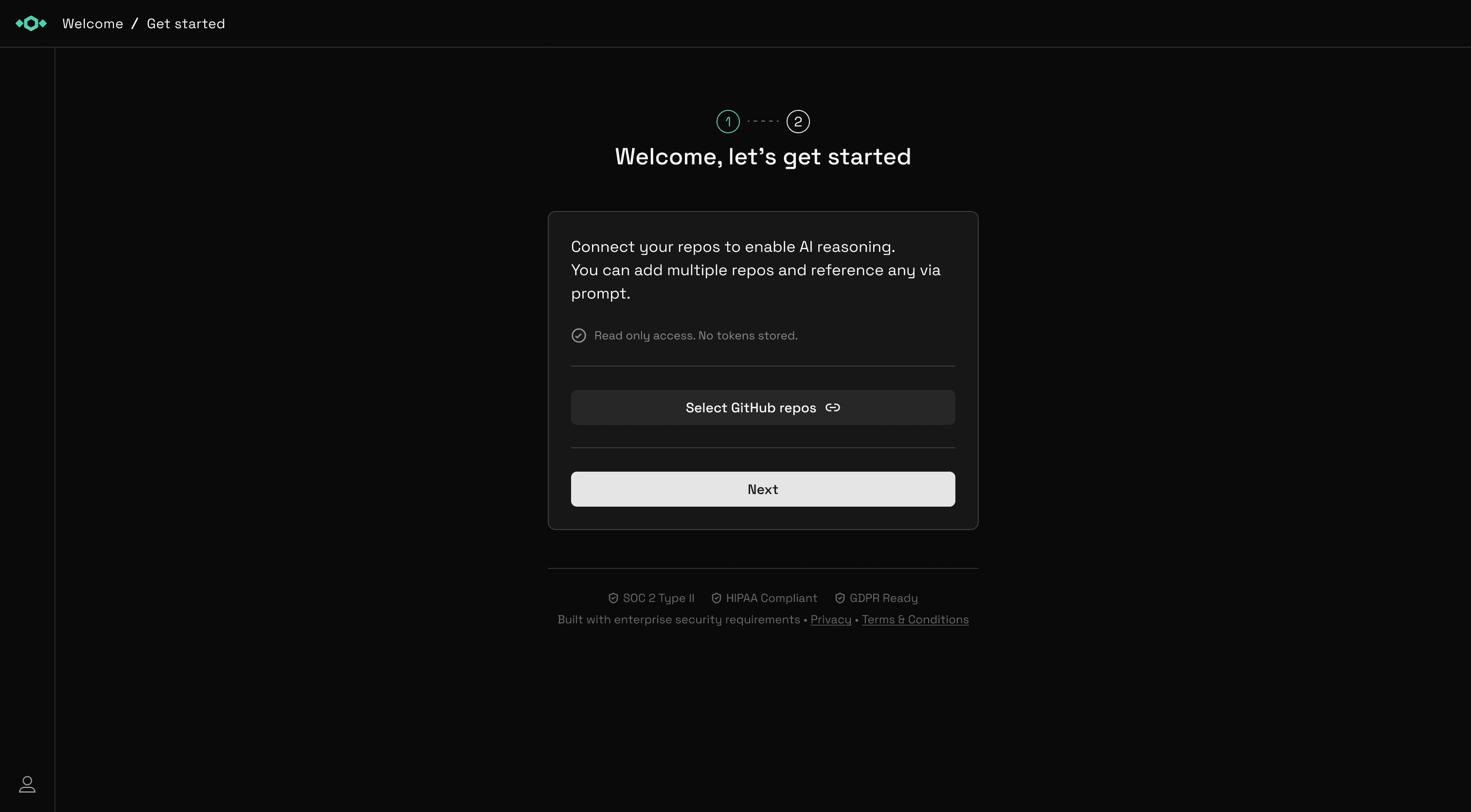
Authorize GitHub Access
Click "Connect GitHub" and authorize Tetrix AI in the GitHub OAuth flow. You'll be asked to grant repository access and webhook management permissions.
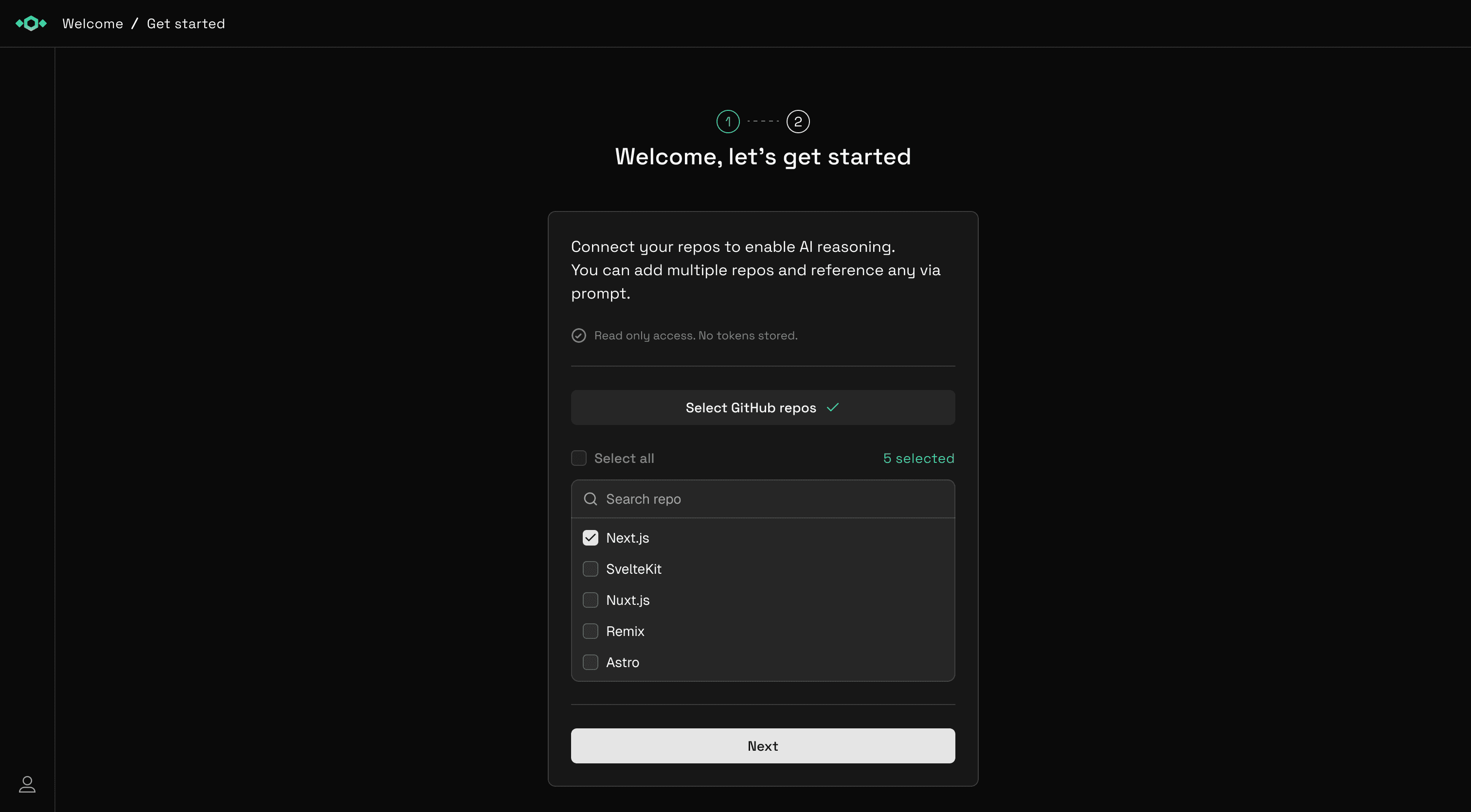
Select Repositories
Choose which repositories you want to analyze. You can:
- Select individual repositories
- Choose all repositories from an account
- Include organization repositories (if you have access)
Automatic Webhook Setup
Tetrix automatically configures webhooks for selected repositories. You don't need to manually set up anything—it just works.
Webhooks are configured and your repositories are now being analyzed!
Adding More Repositories
You can add additional repositories at any time after initial setup.
Select GitHub Integration
Click on the GitHub integration to manage your connected repositories.
Add Repositories
Click "Add Repositories" and select additional repos from your GitHub accounts. You can also add repositories from new organizations you've joined.
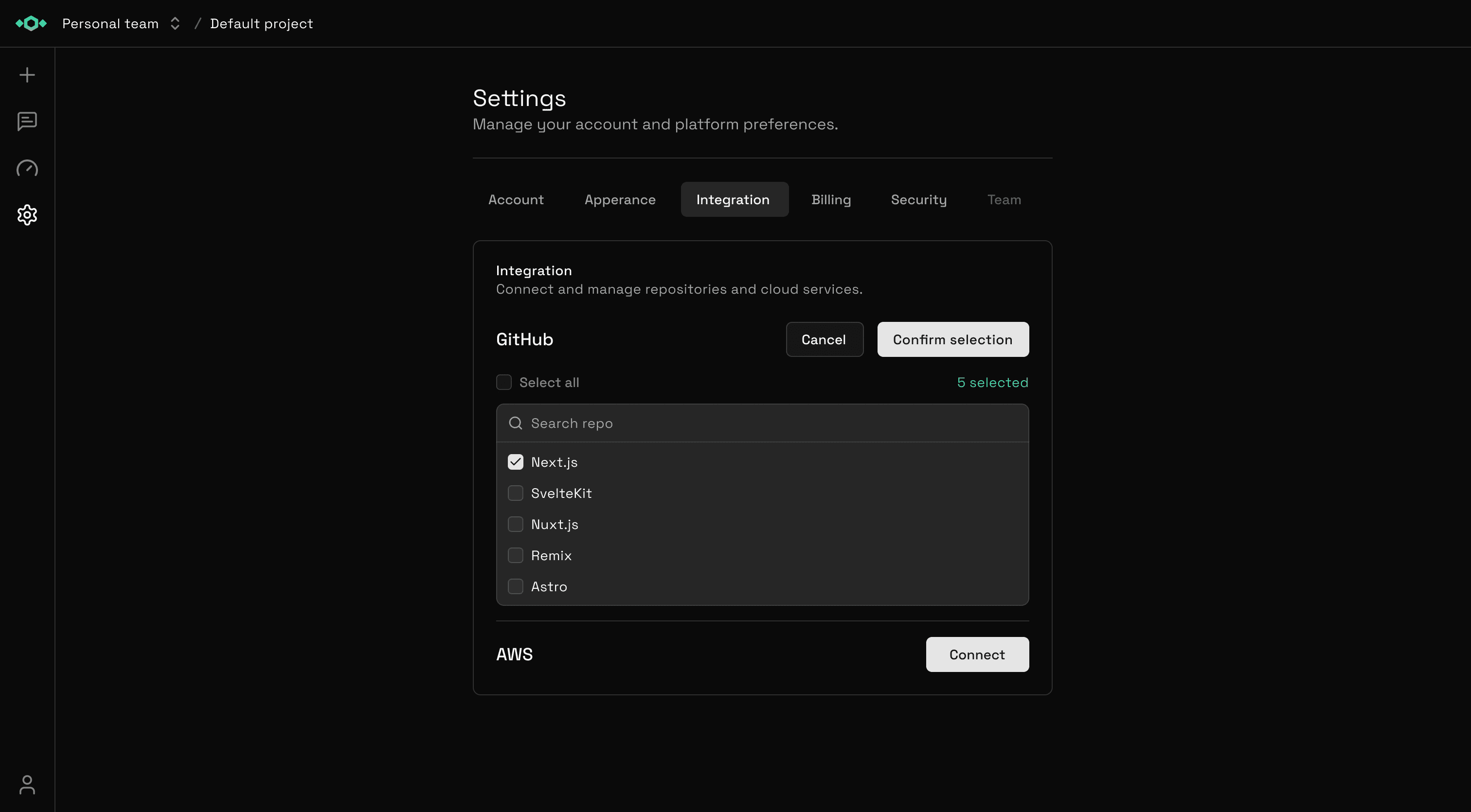
Tetrix will automatically:
- Set up webhooks for new repositories
- Begin analyzing the new codebases
- Update the Knowledge Graph with the new information
- Make the repositories available for queries
Managing Connected Repositories
View Connected Repositories
See all your connected repositories in Settings > Integrations > GitHub.
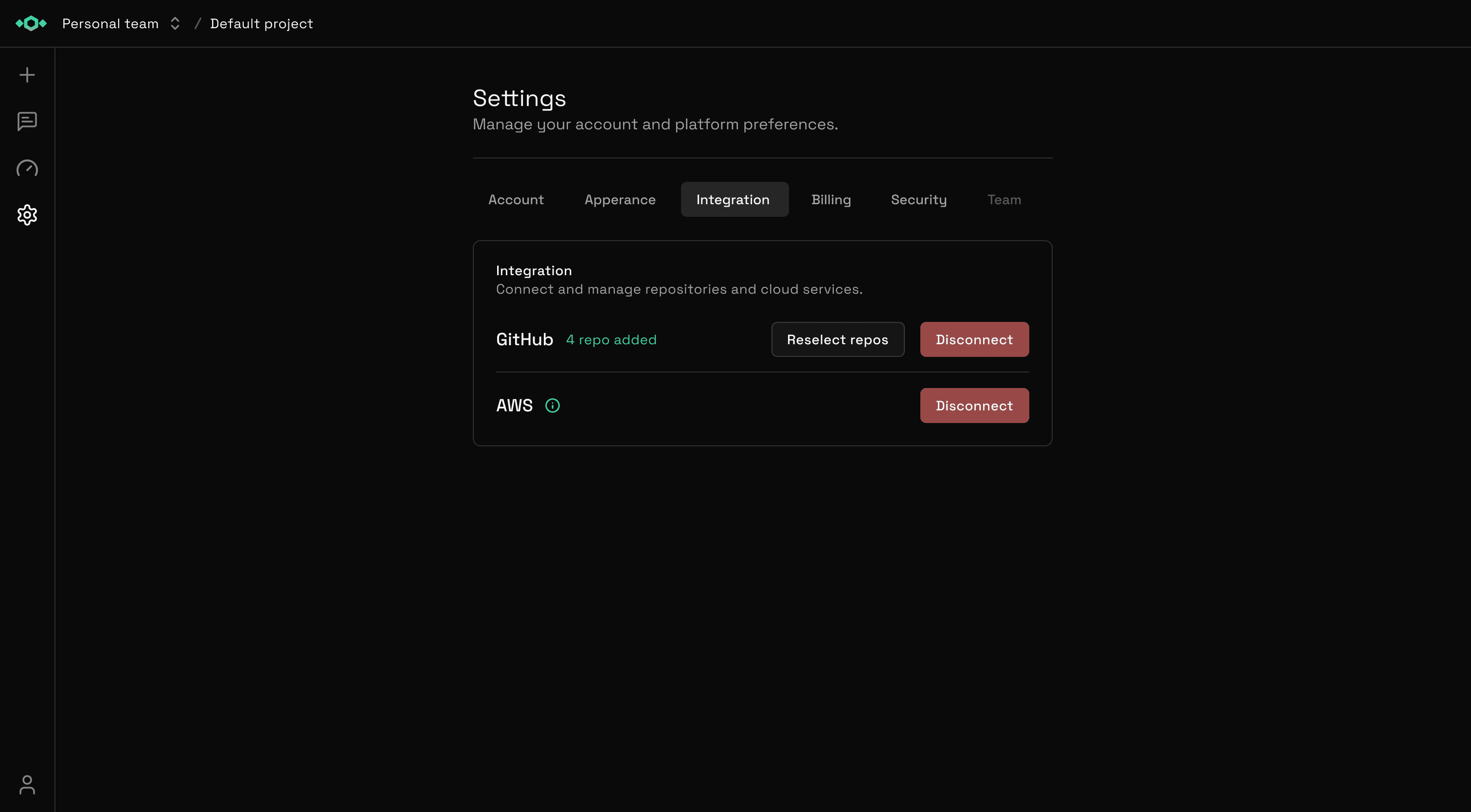
For each repository, you can see:
- Repository name and organization
- Connection status
- Last sync time
- Analysis status
- Webhook health
Remove Repositories
To disconnect a repository:
- Go to Settings > Integrations > GitHub
- Find the repository you want to remove
- Click the remove/disconnect button
- Confirm the action
When you remove a repository, Tetrix will:
- Remove the webhook from GitHub
- Delete the repository data from the Knowledge Graph
- Stop analyzing future changes to that repo
Re-sync Repositories
If you suspect the Knowledge Graph is out of sync:
- Go to the repository in Settings > Integrations
- Click "Re-sync" or "Refresh Analysis"
- Tetrix will perform a fresh analysis of the current repository state
This is useful if:
- Webhook deliveries failed
- Major changes were made outside the main branch
- You want to ensure the latest state is captured
What Tetrix Analyzes
When analyzing your repositories, Tetrix identifies and maps:
Code Structure
- Classes and Interfaces: Object-oriented structure and hierarchies
- Functions and Methods: All callable code and their purposes
- Variables and Constants: Configuration and data definitions
- Imports and Exports: Module dependencies and relationships
API and Routing
- REST Endpoints: All HTTP routes and handlers
- GraphQL Schemas: Types, queries, mutations, and subscriptions
- RPC Methods: gRPC and other remote procedure calls
- Middleware: Authentication, authorization, and request processing
Data Layer
- Database Models: ORM/ODM model definitions
- Schemas: Database table structures and relationships
- Queries: SQL and NoSQL query patterns
- Migrations: Database schema evolution
Configuration
- Environment Variables: Required configurations
- Config Files: YAML, JSON, TOML configuration
- Docker/K8s: Container and orchestration configs
- CI/CD: Build and deployment pipelines
Documentation
- README Files: Project documentation
- Code Comments: Inline documentation and explanations
- API Docs: OpenAPI/Swagger specifications
- Architecture Docs: System design documentation
Real-Time Updates
One of Tetrix's most powerful features is real-time synchronization through GitHub webhooks.
How It Works
You Push Code
When you push commits to any connected repository, GitHub sends a webhook notification to Tetrix.
Tetrix Receives Notification
Our webhook service receives the notification within seconds and queues it for processing.
Incremental Analysis
Tetrix analyzes only the changed files and updates the relevant parts of the Knowledge Graph.
Updated Context
Your AI assistant now has the latest code and can answer questions about recent changes.
Supported Events
Tetrix responds to these GitHub events:
- Push Events: Code pushed to any branch (typically main/master)
- Pull Request Events: When PRs are created, updated, or merged
- Branch Events: Creation or deletion of branches
- Release Events: When you create new releases
By default, Tetrix analyzes changes to your default branch (main/master). You can configure which branches to track in Settings.
Multi-Account Support
Tetrix supports multiple GitHub accounts, perfect for:
- Personal and work accounts
- Multiple organizations
- Client repositories
- Open source contributions
Adding Additional Accounts
- Go to Settings > Integrations > GitHub
- Click "Add Another Account"
- Authorize the new GitHub account
- Select repositories from that account
All repositories from all accounts are:
- Analyzed together in your unified Knowledge Graph
- Available for cross-repository queries
- Separately manageable for permissions and access
Organization Repositories
When connecting organization repositories:
- You must have appropriate permissions in the organization
- Tetrix respects GitHub's organization settings and permissions
- You can only access repositories you have access to in GitHub
- Organization admins can revoke Tetrix access at any time
Troubleshooting
Best Practices
Repository Selection
✅ Do:
- Connect all related repositories in a microservices architecture
- Include infrastructure-as-code repositories
- Add documentation repositories for complete context
- Connect both frontend and backend repositories
❌ Don't:
- Connect repositories you don't actively work on
- Add archived or deprecated repositories
- Include repositories with only binary files
- Connect extremely large monorepos unnecessarily (if only working on part of it)
Webhook Management
✅ Do:
- Let Tetrix manage webhooks automatically
- Check webhook health occasionally in Settings
- Keep your default branch configured correctly
❌ Don't:
- Manually delete Tetrix webhooks from GitHub
- Disable webhooks unless you want to pause analysis
- Change webhook settings manually
Security
✅ Do:
- Review connected repositories regularly
- Disconnect repositories you no longer need analyzed
- Monitor OAuth application access in GitHub settings
- Revoke access immediately if you suspect issues
❌ Don't:
- Share OAuth tokens or credentials
- Connect repositories with sensitive secrets in code
- Use a shared GitHub account for Tetrix
Privacy & Security
Tetrix takes your code privacy seriously. Learn more about our security practices on the Security page.
What we access:
- Repository content for analysis
- Commit history and metadata
- Branch and tag information
- Repository structure and organization
What we DON'T store:
- Full source code content (only structure and relationships)
- Secrets, API keys, or credentials from your code
- Private information in commit messages
- Sensitive data in configuration files
Security measures:
- OAuth-based secure authentication
- Webhook signature verification
- Encrypted data transmission (TLS)
- Isolated per-user data storage
- Regular security audits
Need Help?
If you encounter issues not covered in this guide:
- Support Email: support@tetrix.ai
- Documentation: Check our Concepts page for more background
- Security Questions: See our Security page
For urgent issues or bugs, please include:
- Repository name and organization
- Screenshot of any error messages
- Steps to reproduce the issue
- When the problem started